A Comprehensive Understanding of Direct Store Delivery (DSD)

Direct Store Delivery (DSD) is a distribution method in which manufacturers or suppliers deliver their products directly to retail stores. This system ensures that products are delivered quickly and efficiently while maintaining product freshness, optimizing store-level inventory, and enhancing product visibility at the point of sale. DSD plays a crucial role in industries where products are perishable or have high demand for frequent replenishment.
This distribution method stands in contrast to the traditional route-based distribution model, where products are first sent to a central warehouse or distribution center, then shipped to stores. By bypassing warehouses and delivering products directly to retailers, DSD streamlines the Route-to-Market (RTM) strategy, offering a range of advantages and challenges for businesses in industries such as food and beverages, consumer packaged goods (CPG), dairy, and alcoholic beverages.
What is Direct Store Delivery (DSD)?
At its core, Direct Store Delivery (DSD) is a distribution strategy in which products are shipped directly from the manufacturer or supplier to retail stores. Unlike traditional distribution models where goods are first delivered to distribution centers, DSD skips this intermediary step and delivers products straight to stores, such as supermarkets, convenience stores, and chain retailers.
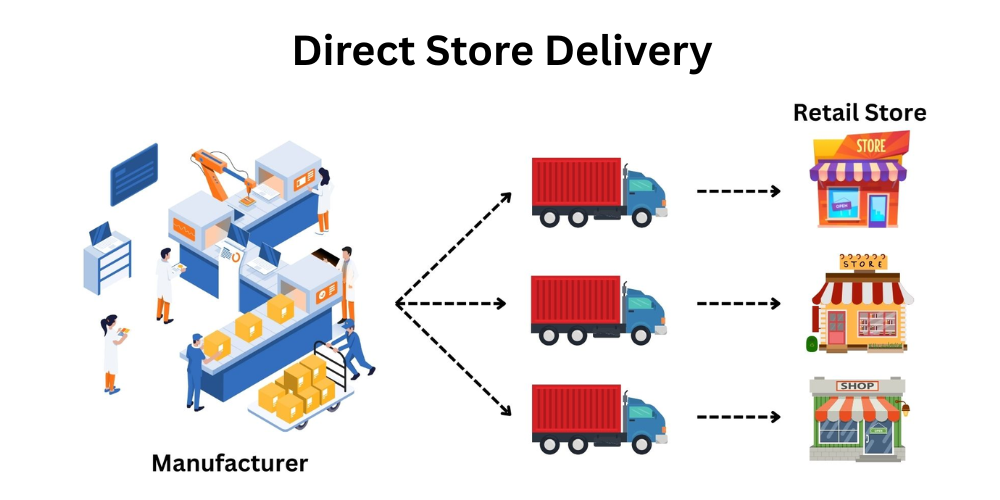
This model is highly effective for companies selling fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), particularly perishable items that require frequent restocking, like dairy, baked goods, snacks, and beverages. DSD ensures that the product reaches the store without delays, thus maintaining the product’s quality, freshness, and availability.
For example, in the case of a snack company, the manufacturer directly delivers boxes of chips and other products to the retail store rather than through a central warehouse. The store receives a delivery at regular intervals, helping to keep the shelves stocked with the latest products and manage inventory levels in real-time.
Key Features of Direct Store Delivery (DSD)
1. Faster Replenishment and Stock Rotation
DSD ensures that products are replenished quickly and frequently. Retailers receive more frequent shipments of products based on the store’s actual sales and demand, rather than on a bulk order from a distribution center. This leads to faster stock replenishment, which is essential for products that have a short shelf life.
For instance, perishable products like dairy or fresh bread need to be delivered regularly to ensure freshness and reduce waste. By receiving deliveries directly from the supplier, these products are restocked as needed, keeping store shelves fresh and reducing the likelihood of stockouts.
Moreover, this system facilitates efficient stock rotation, as the supplier has direct visibility into the store's inventory. The retailer can focus on selling older stock while adding the newly delivered items.
2. Control Over Product Placement and Merchandising
In the DSD model, suppliers often retain control over how their products are displayed and promoted in the store. This is a key feature because it ensures that products are displayed optimally to catch customers' attention. In contrast, with traditional distribution, retailers are responsible for the placement and merchandising of products, which may not always align with the manufacturer’s marketing strategy.
For example, a beverage supplier might want to ensure its soda brand is prominently displayed in the store’s cooler or positioned near the checkout to boost impulse purchases. By controlling the placement and promotional materials (such as banners and signage), suppliers can better manage brand visibility and create more effective marketing campaigns.
3. Reduced Inventory Risk
By handling inventory directly at the store level, suppliers can ensure that their products are stocked in quantities that match demand, thus minimizing the risks of stockouts or overstocking. Through the DSD system, the supplier has better control over the amount of product in each store and can make necessary adjustments as demand fluctuates.
This reduces the risk of excess stock sitting on shelves or, conversely, running out of product altogether, which could result in missed sales. For retailers, this means more consistent product availability and a more reliable inventory system.
4. Lower Transportation Costs
For suppliers, DSD can offer reduced transportation costs by eliminating the need for an additional step in the distribution process. Traditional distribution methods require transporting goods to a central warehouse before further shipping them to various retail locations. DSD, on the other hand, involves direct delivery from the manufacturer to the store, which can streamline transportation and reduce the associated costs.
However, there are cases where transportation costs may rise due to the frequency of deliveries. For example, if a supplier is delivering small quantities of goods to a large number of stores on a daily or weekly basis, the transportation costs per delivery could increase. This needs to be carefully managed to ensure that the benefits outweigh the costs.
Benefits of Direct Store Delivery (DSD)
1. Improved Freshness of Products
In industries like food and beverages, the freshness of products is crucial. With DSD, suppliers can ensure that their products are delivered directly to stores as quickly as possible, minimizing time spent in warehouses and reducing the risk of product spoilage.
For example, dairy products like milk or yogurt have limited shelf lives. A DSD system ensures that these products are regularly restocked and replaced with fresh stock, ensuring that customers always have access to fresh products.
2. Enhanced Store-Level Control for Manufacturers
DSD allows manufacturers to have greater control over how their products are handled and presented in stores. For brands, this is a vital factor as it allows them to implement specific merchandising strategies that might be lost in the traditional distribution system, where the retailer controls stock levels and display.
Retailers and manufacturers can also work closely on promotions, seasonal sales, and in-store marketing campaigns to push products to consumers. This increased collaboration helps suppliers improve their market share and visibility within specific retail locations.
3. Higher Sales and Customer Satisfaction
The DSD model can help boost sales by ensuring that products are constantly available in stores, reducing the likelihood of customers encountering out-of-stock items. Additionally, by ensuring that products are well-displayed, manufacturers can increase product visibility and entice consumers to make purchases.
Frequent restocking and fresh products contribute to a better shopping experience. Consumers are more likely to return to a store where they consistently find the products they want, which in turn improves customer satisfaction and loyalty.
4. Flexibility for Retailers
DSD offers greater flexibility for retailers because it reduces the dependency on centralized warehouses. Stores can place smaller, more frequent orders and work with suppliers to adjust deliveries as needed.
Moreover, DSD empowers retailers to better align with modern Route-to-Market (RTM) strategies, ensuring that products are delivered through the fastest and most efficient channels based on customer demand patterns.
Challenges of Direct Store Delivery (DSD)
Many of the challenges associated with direct store delivery such as logistics complexity, inventory inaccuracies, and coordination gaps can be addressed through digital transformation. Using route planning tools, real-time inventory visibility, and sales force tracking software helps businesses streamline DSD operations and reduce operational risks.
-1766556145.png)
1. Coordination and Logistical Complexity
While DSD has numerous benefits, it also introduces complexity into logistics. Coordinating deliveries from multiple suppliers to different retail locations requires efficient scheduling and communication between the supplier, retailer, and delivery personnel.
For large retailers with hundreds or thousands of stores, managing the flow of goods through the DSD model can be challenging. Additionally, DSD involves tracking numerous products with varying shelf lives and storage requirements, which adds another layer of complexity to inventory management.
2. Higher Transportation and Distribution Costs
While DSD can offer cost savings by eliminating warehouses, it may also result in higher transportation costs due to the need for frequent deliveries. Delivering small quantities of products to many locations on a regular basis can be less efficient compared to shipping larger quantities to a central warehouse.
Additionally, because manufacturers are responsible for transportation, they may need to invest in their own fleet of vehicles or rely on third-party carriers, which can lead to increased operational costs.
3. Potential for Stockouts and Inaccurate Inventory
If suppliers do not have real-time access to store inventory data or fail to keep track of delivery schedules, DSD can lead to stockouts or excess inventory. This could result in missed sales opportunities or wasted products, particularly if perishable goods expire before being sold.
For retailers, poor coordination between the store and supplier can cause disruptions in inventory management, leading to either running out of popular items or overstocking products that aren’t selling well.
4. Limited Visibility Into Field Sales and Delivery Execution
In traditional or poorly digitized DSD setups, businesses often lack real-time visibility into field sales and delivery activities. Managers may not know whether planned store visits were completed, routes were followed correctly, or promotions were executed as intended.
This limited visibility makes it difficult to measure field productivity, identify bottlenecks, or take corrective action quickly, impacting overall DSD performance and accountability.
5. Manual Processes and Data Entry Errors
Many DSD operations still rely on manual order taking, handwritten invoices, and delayed data entry. These manual processes increase the risk of errors in order quantities, pricing, discounts, and delivery records.
Even small inaccuracies can lead to billing disputes, delayed deliveries, and inventory mismatches, ultimately affecting retailer trust and operational efficiency.
6. Difficulty in Managing Promotions and Trade Schemes
Executing promotions effectively in a DSD model can be challenging, especially when sales teams manage multiple stores across different routes. Without proper tracking, promotional offers may be inconsistently applied, leading to revenue leakage or retailer dissatisfaction.
Lack of visibility into promotional performance also makes it harder for businesses to evaluate the success of trade promotions at the store level.
7. Scalability Challenges as Operations Grow
While DSD works efficiently at a smaller scale, expanding operations to new regions or increasing the number of retail outlets can strain existing systems. More routes, vehicles, sales representatives, and SKUs increase operational complexity.
Without scalable processes and supporting technology, businesses may struggle to maintain service levels, delivery accuracy, and cost efficiency as DSD operations grow.
8. Compliance and Accountability Issues
Ensuring compliance with delivery schedules, pricing policies, and merchandising standards is another challenge in DSD operations. When processes are not tracked digitally, it becomes difficult to verify whether field teams are following standard operating procedures.
This lack of accountability can lead to inconsistencies in store execution, missed visits, and reduced brand presence across retail outlets.
While these challenges are common in direct store delivery models, they can be effectively addressed through the adoption of digital tools such as route optimization, real-time inventory management, and field sales automation software.
Direct Store Delivery (DSD) vs. Tr\aditional Distribution
The following table highlights the key differences between Direct Store Delivery (DSD) and traditional distribution models.
-1766556297.png)
|
Feature |
Direct Store Delivery (DSD) |
Traditional Distribution |
|
Delivery Method |
Direct from manufacturer to retailer |
From manufacturer to distributor to retailer |
|
Inventory Management |
Managed by the supplier directly at the store |
Managed by distributor or warehouse |
|
Frequency of Deliveries |
More frequent, smaller batches |
Less frequent, larger shipments |
|
Product Types |
Perishable, fast-moving goods |
Non-perishabl e, seasonal goods |
|
Control Over Display |
Supplier manages product placement |
Retailer manages in-store displays |
Direct Store Delivery vs Direct Delivery: Key Differences
While direct store delivery (DSD) and direct delivery are related concepts in logistics, they serve different purposes and applications. Understanding the distinctions between the two helps businesses choose the right distribution strategy for their products, optimize supply chain efficiency, and improve in-store operations.
The table below highlights the key differences between Direct Store Delivery (DSD) and Direct Delivery across several important aspects:
|
Feature |
Direct Store Delivery (DSD) |
Direct Delivery |
|
Definition |
A specialized distribution method where products are delivered directly from the manufacturer or supplier to retail stores, bypassing warehouses. |
A broad distribution method where products are delivered straight from the manufacturer or supplier to the end destination, bypassing intermediaries. |
|
Focus |
Optimizing in-store operations, maintaining product freshness, and controlling merchandising at the retail level. |
Reducing supply chain steps and improving speed and efficiency in logistics across various sectors. |
|
Application |
Primarily used in retail, especially for perishable goods like dairy, baked items, snacks, and beverages. |
Can be used in retail, wholesale, B2B, or any scenario requiring direct shipment to the end point. |
|
Delivery Frequency |
Frequent and smaller deliveries based on store demand. |
Flexible; may involve larger or less frequent shipments depending on logistics needs. |
|
Inventory Control |
Suppliers often manage stock levels and rotation directly at the store. |
Inventory may be managed by the recipient or through other logistics arrangements. |
|
Objective |
Improve product availability, freshness, shelf visibility, and sales at retail stores. |
Ensure faster delivery and efficiency throughout the supply chain. |
This comparison allows businesses to leverage the advantages of each model effectively. While DSD is highly effective for perishable and fast-moving consumer goods where store-level control is essential, direct delivery provides a broader logistics solution that improves supply chain speed and efficiency across multiple industries.
How Technology is Transforming Direct Store Delivery ?
Traditional DSD models relied heavily on manual processes, paper invoices, and limited visibility into store-level performance. Today, technology-driven DSD solutions are transforming how manufacturers and distributors manage direct store delivery operations.
Modern DSD software enables real-time inventory tracking, automated order capture, GPS-based route optimization, and instant sales reporting. Field sales representatives can place orders directly from retail stores using mobile devices, ensuring faster replenishment and accurate demand forecasting.
By leveraging field sales automation platforms like Delta Sales App, businesses can gain end-to-end visibility into their DSD operations from van stock management to outlet-level performance while reducing errors, improving delivery efficiency, and avoiding stockouts.
Conclusion
Direct Store Delivery (DSD) is a highly effective distribution model, particularly for industries dealing with perishable products or high-demand goods that require frequent replenishment.
By bypassing traditional distribution centers and shipping products directly from the manufacturer to the store, DSD supports a faster Route-to-Market approach, providing numerous benefits, including fresher products, improved stock rotation, and better control over product placement.
However, DSD comes with its challenges. The logistics involved in DSD can be efficiently supported by Trade Promotion Management Apps, which help companies coordinate promotions, optimize in-store execution, and avoid stockouts during major campaigns.
Want to see how Direct Store Delivery can work seamlessly for your business?
Book a demo of Delta Sales App to experience real-time inventory tracking, route optimization, and field sales automation designed specifically for DSD and FMCG distribution.
FAQ
1. What is Direct Store Delivery (DSD)?
Direct Store Delivery (DSD) is a distribution method where manufacturers or suppliers deliver products directly to retail stores, bypassing warehouses or distribution centers. It helps maintain product freshness, improve stock availability, and increase sales.
2. What are the advantages of Direct Store Delivery?
DSD offers several benefits, including faster product replenishment, improved product freshness, better control over merchandising, enhanced customer satisfaction, and reduced inventory risks for retailers and manufacturers.
3. What types of products are best suited for DSD?
Products that are perishable or require frequent restocking, such as dairy items, baked goods, snacks, beverages, and fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), are ideal candidates for Direct Store Delivery.
4. How is Direct Store Delivery (DSD) different from traditional distribution?
In DSD, products are delivered directly from the manufacturer to the retail store, while traditional distribution involves sending goods to a central warehouse first and then to stores. DSD allows more frequent deliveries and better control over product placement.
5. What are the challenges businesses face with DSD?
The main challenges include higher transportation costs, increased logistical complexity, coordination difficulties across multiple stores, and the risk of stockouts if inventory data is not accurately tracked.
Also Check:
👉 Beat and Route Plan in FMCG Sales
👉 Top 5 Emerging Trends in Sales Distribution Channels You Need to Know
See What Users Say About Us!
Our Delta Sales App, trusted by businesses for inventory and sales management, is highly rated on leading review platforms.
You can check what real users are saying about us:
Experience why Delta Sales App is the preferred choice for Field Sales Automation Software and can also support your Trade Promotion Management initiatives!










