Beat Plan vs. Daily Planning: How to Structure Your Field Sales Team's Visits

In today’s highly competitive and execution-driven sales environment, the effectiveness of a field sales team is defined not by effort alone, but by how intelligently that effort is planned and deployed. As organizations scale their distribution networks and expand their retail footprint, structuring sales visits becomes a strategic necessity rather than an operational afterthought.
Understanding the difference between Beat Plan vs. Daily Planning is critical for sales leaders, operations managers, and distribution heads who want to maximize coverage, improve market execution, and drive consistent revenue growth.
This blog explores both approaches in detail, compares their strengths and limitations, and provides guidance on how to structure your field sales team’s visits effectively.
Understanding Field Sales Visit Planning
Field sales visit planning refers to the structured process of deciding which customers to visit, when to visit them, and how frequently while considering geography, priority, workload, and business objectives.
In traditional sales environments, visit planning often relied on manual schedules, individual judgment, and static routes. However, modern sales ecosystems demand more accuracy, predictability, and accountability. Poor planning leads to missed outlets, uneven coverage, wasted travel time, and inconsistent customer engagement.
This is where Beat Plans and Daily Planning frameworks come into play each offering a distinct approach to organizing field sales activity.
What Is a Beat Plan?
Beat Plan is a predefined, recurring visit schedule that assigns specific customers or territories to sales representatives on fixed days or cycles. It creates a structured rhythm of visits that repeats weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly.
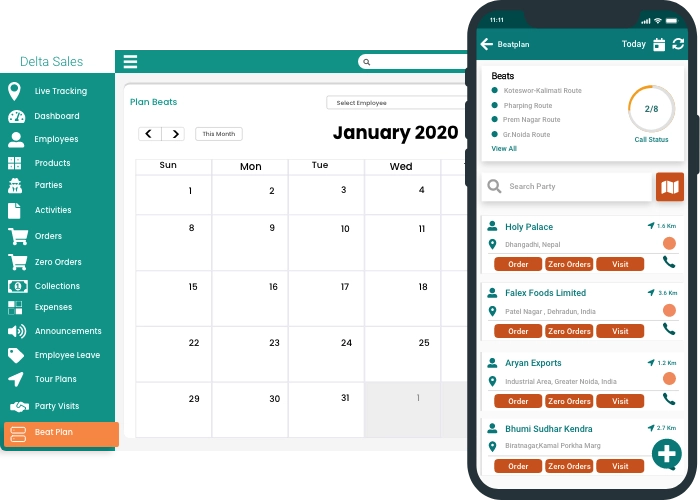
In a beat plan model, each sales representative follows an assigned “beat” or route, ensuring consistent coverage of designated outlets. This approach is widely used in industries such as FMCG, pharmaceuticals, distribution, and retail-heavy sales models.
Key Characteristics of a Beat Plan
-
Fixed visit schedules for customers or outlets: Sales representatives follow predefined visit days and frequencies, ensuring every outlet is covered regularly without missed visits or irregular customer engagement.
-
Predetermined routes and territories: Each salesperson is assigned a specific geographic area and route, reducing travel time, avoiding overlap, and enabling efficient territory-level sales execution.
-
Repetitive and predictable sales cycles: Visits occur in a recurring pattern, creating consistency in ordering, replenishment, and relationship-building while simplifying planning and performance forecasting.
-
Strong alignment with distribution and supply planning: Predictable visit cycles help distribution teams plan inventory, replenishment, and logistics more accurately, reducing stock-outs and improving overall supply chain efficiency.
-
High control and visibility for managers: Managers can easily monitor adherence, coverage, and productivity, identify deviations quickly, and ensure standardized execution across regions and teams.
-
Effectiveness in consistency-driven environments: Beat plans work best where regular presence, fixed purchase patterns, and repeat sales matter more than flexibility, such as FMCG, retail distribution, and high-volume markets.
Advantages of Using a Beat Plan
-
Predictable Market Coverage: Beat plans ensure that every outlet is visited at a fixed frequency. This eliminates the risk of over-serving some customers while neglecting others.
-
Operational Discipline: With a predefined schedule, sales representatives develop routine, discipline, and accountability. Managers can easily track adherence and identify deviations.
-
Efficient Route Optimization: Sales teams follow optimized routes that reduce travel time and fuel costs, improving daily productivity.
-
Better Demand Forecasting: Since visits occur on predictable cycles, organizations can plan inventory, replenishment, and promotions more effectively.
-
Scalability Across Large Teams: Beat plans are easier to replicate and standardize across regions, making them ideal for large field forces.
Limitations of Beat Planning
While effective, beat plans are not without challenges:
-
Limited flexibility to respond to urgent opportunities: Fixed schedules make it difficult for sales representatives to adjust visits quickly when urgent orders, high-potential leads, or unexpected customer demands arise.
-
Difficulty adjusting to sudden market changes: Beat plans struggle to accommodate rapid changes such as competitor actions, pricing shifts, promotions, or sudden demand fluctuations within the market.
-
Potential inefficiency if outlet priorities shift
When outlet potential changes, fixed routes may result in time spent on low-value customers while high-growth or priority outlets receive insufficient attention. -
Risk of routine fatigue among sales representatives: Repeated routes and identical schedules can reduce motivation over time, leading to disengagement, lower enthusiasm, and reduced effectiveness during customer interactions.
-
Restricted agility in fast-changing markets: In dynamic environments, rigid beat structures may prevent sales teams from acting quickly, limiting responsiveness and slowing down revenue or relationship opportunities.
In fast-changing markets, rigid beat plans may restrict agility.
What Is Daily Planning?
Daily Planning is a dynamic, flexible approach where sales representatives or managers plan visits on a day-to-day basis rather than following a fixed recurring schedule.
In this model, daily priorities, customer needs, sales targets, and real-time inputs drive visit decisions. Daily planning is commonly supported by digital sales tools that provide visibility into outlet performance, pending orders, and route feasibility.
Key Characteristics of Daily Planning
-
Flexible visit schedules: Sales representatives plan visits daily based on priorities, allowing adjustments to routes and customers according to changing business needs, opportunities, or operational constraints.
-
Real-time decision-making: Visit plans are created using live information such as orders, stock levels, and customer requests, enabling quick responses to market conditions and immediate sales opportunities.
-
Priority-driven customer selection: Customers are chosen based on urgency, revenue potential, or strategic importance, ensuring sales efforts focus on high-impact accounts rather than fixed schedules.
-
Greater autonomy for sales reps: Sales representatives have more control over planning their day, encouraging ownership, accountability, and better alignment between individual judgment and business goals.
-
Strong reliance on data and insights: Daily planning depends heavily on CRM, SFA, and analytics data to identify priorities, optimize routes, and guide informed, performance-driven visit decisions.
-
Adoption in dynamic sales environments: Daily planning is widely used in B2B sales, key account management, and emerging markets where customer needs, deal timelines, and priorities change frequently.
Advantages of Daily Planning
High Flexibility:Sales teams can respond immediately to urgent orders, stock-outs, competitive activity, or new opportunities.
Customer-Centric Approach: Visits are planned based on actual needs rather than predefined schedules, improving customer satisfaction.
Better Resource Utilization: Sales reps can focus on high-potential accounts and avoid low-value visits.
Alignment With Real-Time Data: Daily planning works best when supported by CRM, SFA, or analytics tools that provide actionable insights.

Encourages Ownership and Accountability: Sales representatives take greater responsibility for planning and prioritizing their day.
Limitations of Daily Planning
Despite its flexibility, daily planning has its drawbacks:
-
Risk of uneven territory coverage: Daily planning may result in some areas or outlets being visited frequently while others are overlooked, leading to inconsistent market coverage and missed revenue opportunities.
-
Potential bias in outlet selection: Sales representatives may prioritize familiar or easier customers over strategically important ones, causing imbalance and reduced focus on long-term growth accounts.
-
Higher dependency on individual discipline: Effective daily planning relies heavily on each salesperson’s planning skills and commitment, making performance inconsistent if discipline or accountability is lacking.
-
Difficult to scale without strong digital systems: As teams grow, managing daily plans becomes complex without robust CRM or SFA tools to provide visibility, coordination, and standardized execution.
-
Increased management complexity: Managers must continuously monitor plans, priorities, and outcomes, increasing oversight effort and making performance tracking more challenging than fixed planning models.
-
Risk of inconsistent execution without controls: Without clear guidelines, monitoring, and data-driven guardrails, daily planning can lead to unpredictable sales activities and uneven results across teams and regions.
Beat Plan vs. Daily Planning: A Comparative View
When comparing Beat Plan vs. Daily Planning, the differences become clear across multiple dimensions:
|
Aspect |
Beat Plan |
Daily Planning |
|
Structure |
Fixed and repetitive |
Dynamic and flexible |
|
Coverage |
Consistent and predictable |
Variable and priority-based |
|
Flexibility |
Low |
High |
|
Scalability |
High |
Moderate |
|
Managerial Control |
Strong |
Relatively lower |
|
Responsiveness |
Limited |
excellent |
|
Best For |
FMCG, retail distribution |
B2B, key accounts, emerging markets |
This comparison highlights that neither approach is universally superior, the right choice depends on business objectives, market maturity, and team structure.
How to Choose the Right Planning Model
-
Assess Market Complexity: Stable, high-volume retail environments benefit from beat plans, while volatile or relationship-driven markets require daily planning.
-
Evaluate Team Size and Geography: Large teams covering dense retail networks need structured beat plans to maintain discipline. Smaller or specialized teams can thrive with daily planning.
-
Consider Product and Sales Cycle: Fast-moving, repeat-purchase products align well with beat plans. Long sales cycles and customized offerings favor daily planning.
-
Review Digital Readiness: Daily planning demands strong data visibility and mobile-enabled tools. Without digital support, beat planning is safer and more controllable.
-
Analyze Customer Segmentation: If customers vary significantly in size, value, or service needs, daily planning helps prioritize high-value accounts, while beat plans suit uniform, volume-driven customer bases.
-
Evaluate Frequency of Customer Interaction: Businesses requiring frequent, routine visits benefit from beat plans, whereas infrequent or need-based customer interactions are better managed through daily planning.
-
Assess Managerial Control Requirements: Organizations needing tight monitoring, standardized execution, and compliance may prefer beat plans, while mature teams with experienced reps can handle daily planning autonomy.
-
Consider Speed of Decision-Making: Markets demanding rapid responses to stock-outs, competitor actions, or pricing changes are better supported by daily planning than rigid beat structures.
-
Review Sales Team Skill Levels: Less-experienced teams benefit from the guidance of beat plans, while skilled, self-directed sales representatives perform effectively with daily planning flexibility.
-
Factor in Growth and Scalability Goals: If rapid expansion or onboarding of new sales reps is planned, beat plans provide a scalable framework. Daily planning suits stable teams with manageable growth rates.
The Hybrid Approach: Combining Beat Plan and Daily Planning
Many high-performing organizations no longer treat Beat Plan vs. Daily Planning as a binary choice. Instead, they adopt a hybrid planning model that blends structure with flexibility.
How Hybrid Planning Works
-
Core outlets follow a fixed beat plan: High-volume or strategically important outlets are visited on predefined schedules, ensuring consistent coverage, predictable sales cycles, and disciplined execution across core markets.
-
High-priority or exception accounts are planned daily: Urgent, high-potential, or special-case accounts are managed through daily planning, allowing sales teams to respond quickly to opportunities, issues, or changing customer needs.
-
Managers set guardrails while allowing rep-level adjustments: Leadership defines rules, priorities, and coverage expectations while giving sales representatives flexibility to adjust visits within approved boundaries.
-
Digital tools provide visibility and control: Sales automation and analytics platforms enable real-time tracking, route optimization, and plan-versus-actual monitoring, ensuring both flexibility and managerial oversight.
-
Consistency with agility balance: By combining structured beats with flexible daily planning, organizations achieve reliable market coverage while remaining responsive to fast-changing business conditions.
Role of Technology in Modern Visit Planning
Advanced field sales platforms play a crucial role in making both beat plans and daily planning effective. Key capabilities include:
-
Automated route optimization: Technology automatically designs efficient travel routes based on location, visit priorities, and traffic patterns, reducing travel time, costs, and fatigue for field sales representatives.
-
Outlet prioritization based on data: Sales platforms analyze historical sales, order frequency, and outlet performance to rank customers, ensuring high-potential outlets receive timely and focused sales attention.
-
Real-time activity tracking: Managers gain live visibility into sales visits, check-ins, orders, and movement, enabling accurate monitoring of field execution and immediate corrective actions when required.
-
Plan vs. actual performance analysis: Systems compare planned visits with actual execution, highlighting gaps, deviations, and productivity levels to improve accountability and optimize future planning decisions.
-
Manager dashboards and alerts: Centralized dashboards and automated alerts help managers track KPIs, identify risks early, and take quick decisions to improve field sales performance.
Technology eliminates manual guesswork and ensures planning decisions are data-driven.
Conclusion
The debate around Beat Plan vs. Daily Planning is not about choosing one over the other—it is about aligning visit planning with business strategy, market realities, and operational maturity.Beat plans deliver discipline, predictability, and scalability, while daily planning enables flexibility, responsiveness, and a customer-centric approach.
With advanced platforms like the Delta Sales App, businesses can seamlessly manage beat plans, enable smart daily planning, and gain real-time visibility into field execution all from a single, unified system. By leveraging the right planning framework supported by data, technology, and accountability, organizations can transform field sales teams into high-performance revenue drivers.
Book a Delta Sales App Demo Today and empower your field team with real-time insights and optimized routes.










